1. NetSuite Supply Chain Management enhances efficiency by integrating demand planning, procurement, manufacturing, and inventory management, resulting in streamlined operations and optimized resource utilization.
2. The platform enables real-time visibility across the supply chain, allowing businesses to make data-driven decisions and reduce operational risks.
3. NetSuite supports multi-location inventory management, providing centralized control over stock levels across various warehouse and distribution centers.
4. Automated procurement processes in NetSuite reduce manual errors, improving vendor relationships and ensuring timely supply deliveries.
5. The demand forecasting feature uses historical and current data to align inventory levels with market needs, minimizing overstock and shortages.
Financial leverage ratio is a compass that guides organizations in their borrowing and investment decisions.
It is all about the amount of borrowed money a company depends on versus its own.
It is a measurement that compares the borrower’s capital in relation to their assets or liabilities.
Let’s talk about this in detail.
Financial Leverage Ratio Definition
Financial leverage ratios are pivotal indicators for banks and businesses regarding how assets are financed through debt or equity.
Nonetheless, you’ll hear this term more often from market analysts and investors, who assess how easily a company can meet its financial obligations.
But the question remains. What is a leverage ratio?
It is simply the proportion of debt in comparison to equity or capital. A company’s financial leverage ratio represents the debt level compared to its accounts, like income statements, balance sheets, or cash flow statements.
Why is it important for small businesses?
Financial Leverage is one of the most significant tools small businesses use. Reason? There are plenty:
- Increase Returns: Small businesses can yield a higher return on equity (ROE) by using debt to finance assets. That wouldn’t be the case if they financed all assets with equity. And why is that, you may ask? In simple terms, the interest expense on debt is far less than equity cost.
- Faster Growth: Small businesses can scale higher and expand operations quicker than they could if they solely relied on equity financing.
- Enhanced Financial Flexibility: A healthy debt level equals better financial flexibility for small businesses. This provides businesses with a funding source to weather financial storms.
- Tax advantages: Interest payments on debt are actually tax deductible. Thus, debt can minimize a company’s tax liabilities while raising earnings.
Financial Leverage Ratio Formula
Market analysts, lenders, creditors, and investors can consider multiple leverage ratios. But here are the most usual leverage ratio formulas they will talk about:




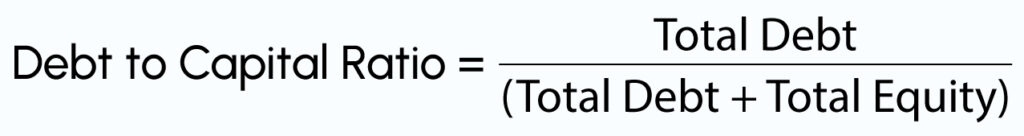
4 Types of Financial Leverage Ratios
We have explained in detail the financial leverage ratios that are important for small businesses. Take a look below!
1. Debt-to-Assets Ratio
This ratio compares the short-term and long-term debt obligations to the total assets of a company. For a fact, a company with a high Debt-to-Assets ratio usually has a greater debt percentage. In contrast, those with low ratios can have smaller debts than the number of assets.
2. Debt-to-Equity Ratio
Also called the risk ratio, this evaluates the company’s debt, later comparing it to the shareholder’s equity. Put simply, this is the ratio creditors and analysts use to understand how a company balances debt and equity in order to support operations and growth.
A higher Debt-to-Equity ratio means a company has been quite fierce while financing its growth with equity. Conversely, a lower ratio represents that a company funds its operations with greater equity than debt. While this is safer, it could also mean less leverage opportunity.
3. Debt-to-Capital Ratio
As the name suggests, this ratio calculates and compares a company’s financial liabilities to its total capital. Companies use this calculation to understand how much debt they use to fund their operations compared to capital. In this case, a higher ratio shows that a more significant portion of the capital is built of debt. That suggests greater leverage and increased financial risk. A lower ratio, on the other hand, implies that the company depends more on equity than debt.
4. Debt-to-EBITDA Ratio
Earnings before interest, taxes, depreciation, and amortization (EBITDA) help measure cash flow to understand the company’s financial standpoint. Besides capital structure, this metric doesn’t necessarily consider particular non-cash expenses to represent a company’s finances. Nonetheless, a high Debt-to-EBITDA Ratio can potentially mean that the organization has a greater debt burden.
How to Calculate Financial Leverage Ratio?
You can use one of the leverage ratio formulas discussed previously to calculate the Financial Leverage Ratio. For better understanding, let’s take the company ABZ Retails, which has the following financial figures:
- $40 M in assets
- $10 M in debt
- $30 M in equity
Now, let’s sit back and evaluate the financial leverage ratios:
- Debt / Equity = $10 M / $30 M = 0.33
- Debt / Assets = $10 M / $40 M = 0.25
- Debt / Capital = $10 M / ($10 M + $30 M) = 0.25
However, the question is: What do these ratios stand for?
To understand better, consider the debt-to-equity ratio. At 0.33, the company is more dependent on equity than debt for funding. This represents a conservative approach to leveraging (here, equity is the primary resource origin).
What is a Good Financial Leverage Ratio?
According to industry standards, a ratio less than 1 is typically considered good. However, if it is higher than 1, lenders and potential investors start believing that the company can potentially be a risky investment. That said, it’s pretty clear how concerning it can be if the ratio hits 2.
4 Key Strategies for Managing and Optimizing Financial Leverage Ratio
As accounting professionals, if you ask us how to improve financial leverage ratio, we might just recommend these 4 strategies.
1. Issue Equity
If a company needs to raise capital, issuing equity might be the best way to go. Consequently, this will boost the company’s equity base, minimizing the debt-to-equity ratio.
2. Enhance Profitability
Companies that are more profitable take up greater debt. How? They can produce the cash flow required to service it. Operational efficiency, for example, is one of the many ways to increase profitability.
3. Purchase Back Stock
Companies have the chance to buy back their own stocks. This, in return, reduces the number of shares outstanding, boosting Earnings Per Share (EPS). How does it benefit you? Well, it makes the company more appealing to investors, thus improving the financial leverage ratio.
4. Use Financial Derivatives
To hedge against risk, companies might also use financial derivatives. For instance, a company, ABZ Retails, can use a swap to lock in an interest rate. That, in return, protects it from gradually increasing interest rates.
Want more strategic financial advice for your business?
Connect with us now
Financial Leverage Ratio Case Study
Example: Financial Leverage in Businesses
Background
Company ABZ Retails operated with significant assets, with a mix of debt and equity financing. Now, let’s look at the company’s financial leverage by using two substantial ratios:
Financial Profile:
- Total Assets: $100 million
- Total Debt: $45 million
- Total Equity: $55 million
Understanding the Analysis
1. Debt-to-Assets Ratio: ABZ Retails indicates quite a moderate reliance on borrowed funds. The Debt-to-Assets ratio appears to be $45M (debt) by $100M (assets). When calculated, the resulting ratio denotes 0.45. This proves that 45% of the company’s assets (less than half) have been financed through debt. This is pretty good information for investors looking to evaluate the company’s financial well-being to make sound decisions.
2. Debt-to-Equity Ratio: The relationship between debt and shareholder equity plays one of the significant roles in deciding a company’s financial well-being. To be more specific, this ratio can show investors and analysts its potential for profitability. For ABZ Retails, ask yourself, “How much debt is consumed for financing the company’s assets in relation to shareholder equity?” When you calculate the Debt-to-Equity Ratio, meaning $45M (debt) by $55M (equity), it gives a total of 0.82. In layman’s language, the company has 82 cents of debt for every equity dollar.
What does this conclude?
ABZ Retails has a balanced financial standing. The setup we see throughout the analysis suggests that the company is tackling leverage very efficiently. Further, it also maintains a stable hold on debt obligations and equity financing.
Summing up
While high leverage can reap big rewards, it can also lead to significant risks. A greater financial leverage ratio implies that the ROI is insufficient to offset the interest paid on debt. As with absolutely any investment strategy, you need to weigh the rewards against the uncertainty before deciding to leverage.
Frankly, understanding financial leverage ratio can unlock financial success for any small business. But, everything comes with a significant upside and a fair share of risks. You can never leave your company to chance. Can you?
Are you looking closely at your financial risks? To make sound decisions, you pretty much have to.
Do you have unanswered questions about Financial Leverage Ratio? Stop lingering around. Get in touch with us today, and our bookkeeping and accounting experts with more than 12 years of experience will give you direct answers. Keep your money safe and your business safer!
Frequently Asked Questions
1. What are some examples of companies with high financial leverage ratios?
There are multiple companies with a higher financial leverage ratio, including:
- Tesla
- Meta
- Netflix
- Amazon
These are high-growth companies and have used financial leverage to maximize growth.
2. What are the risks that come with financial leverage?
You have to be very mindful about financial leverage. If you aren’t, your company can be exposed to interest rate risk and credit risk. When interest rates hike up, a company with a high debt-to-equity ratio needs to pay a greater interest expense. In response, it reduces profitability
3. How can I manage my financial leverage ratio?
For starters,
- Analyze and monitor Debt-to-Equity ratio on a regular basis.
- Set a target Debt-to-Equity ratio to stay on track.
- Take on only what you can afford to pay back.
4. What are some risks associated with financial leverage?
There can be multiple risks you should be aware of:
- Credit risk
- Economic downturn
- Interest rate risk
- Financial instability