1. Bad debt expense is calculated using the allowance method or direct write-off method. The allowance method anticipates losses, while the direct method recognizes them once identified.
2. The formula for bad debt expense is: Total Credit Sales × Estimated Percentage of Uncollectible Accounts. This approach predicts losses and helps maintain accurate financial reporting.
3. Bad debt write-offs involve debiting bad debt expense and crediting accounts receivable. This process adjusts the balance sheet to reflect actual expected receivables.
4. Effective bad debt management involves monitoring receivables aging schedules. This helps classify overdue accounts and proactively reduce potential write-offs.
Has it ever crossed your mind what happens when a customer ends up not paying what they owe?
Just as much as a company books profits, there are undeniably some sorts of losses too. In the group of losses, a company goes through, some are called “bad debt expense”.
A bad debt expense is the cost to a company of its sold goods and services that a customer did not pay for. It is the money that a business is no longer expected to receive, usually because the customer could not afford to pay or seemingly found some discrepancy due to which they simply decided not to pay.
This is typically something that a business occasionally faces, specifically at times when they sell on credit.
What is Bad Debt Expense?
Cash flow is what runs a business, and anything that reduces it jeopardizes the entire game plan of a company.
Any business that offers credit to its clients runs the risk of experiencing a decrease in cash flow or a slowdown in it if any of the credit is used for bad debt expenses.
Bad debt expenses describe the loss a company may face when it realizes that the money it was supposed to receive for delivered goods or services is not going to come in.
In fact, this adjustment also lowers the total accounts receivable (AR), showing only collectible amounts and making sure that the financial statements exhibit the raw financial condition of a company.
Types of Bad Debts
Now that you know what a bad debt expense is, you need to have a clear idea about the several types of bad debts. So, here is a detailed rundown:
1. Uncollectible Accounts Receivable: This is basically a customer debt that a business has tried collecting numerous times but later determined that the amount will most likely never be paid. Read more about 6 steps to collect accounts receivables sooner.
2. Write-offs: This is simply a process where you formally and knowingly remove the “uncollectible” debts from the accounting records. This is where you acknowledge that the amounts will possibly never be recovered.
3. Allowance for Doubtful Accounts: This is a very proactive accounting practice. In simple words, this is where the business keeps aside a specific amount of the total accounts receivable, just predicting that some part of it will not be collectible due to certain reasons.
Want help managing your bad debt expense?
Consult our experienced accountants.
Factors Affecting Bad Debt Expense
There are many external factors that affect bad debt expense. Here are some of the names you will hear more often:
1. Economic Conditions
Economic upheaval or recessions are one of the biggest factors that reduces consumer spending and causes delayed payments. This, in return, increases the likelihood of uncollected debts. On a side note, during economic booms, consumers may have improved liquidity, thus lowering bad debt expense. That is why, you should always look out for current economic trends and predict potential changes in bad debt levels.
2. Industry Standards
Different industries extend credit in a different way, directly exposing them to bad debts. In other words, there are many high-risk sectors that suffer more defaults. This only makes it important for larger bad debt reserves. Having a good grasp on industry-specific credit practices can help you have a fair and realistic expectation for bad debt.
3. Customer Creditworthiness
You can minimize the exposure to risk when you check firsthand the payment history and credit scores of your customers before extending any credit. Once you start regularly assessing the creditworthiness of existing customers, you can reduce bad debt exposure on a whole different level. Read more about credit risk management.
4. Historical Data
Undoubtedly, you can analyze the trends going on from historical payment patterns and past transactions of a given customer. In this way, it becomes far too easy to evaluate future bad debts.
Methods to Estimate Bad Debt Expense
If you’re wondering how to estimate bad debt expense, then there are several methods to do it. Here is a brief rundown:
A. Percentage of Sales Method
This is one of the methods that evaluate uncollectible accounts after applying a certain percentage to total sales. This, in return, exhibits the historical collection experience of the company.
This can be best understood with an example. Let’s say a business had $3,000,000 in sales. They predict that 1.5% of it will be uncollectible. In that case, the bad debt expense is going to be estimated as $45,000 ($3,000,000 x 0.015).
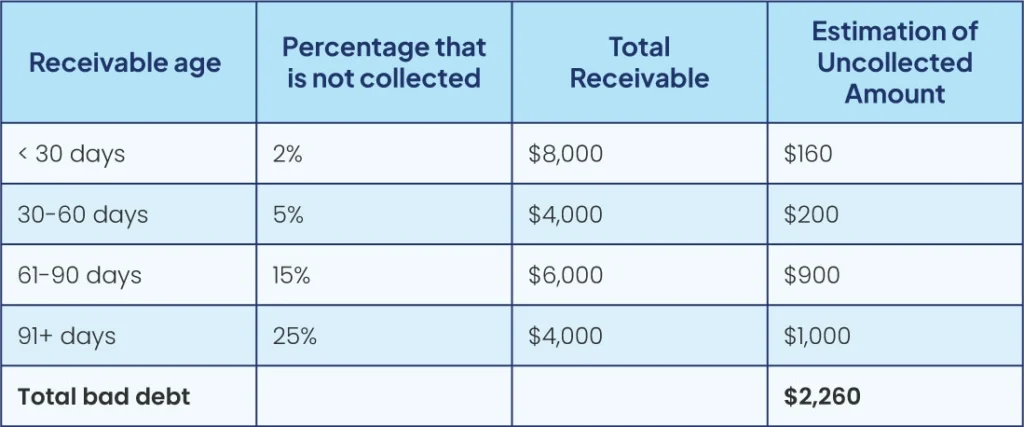
B. Aging of Accounts Receivable Method
The accounts receivable aging method, as the name indicates, is a process that organizes outstanding receivables on the basis of their span and then, applies the percentage on the likelihood of collection. Furthermore, the percentage is going to be derived from the historical collection data of the company.
One of the many pros of the accounts receivable aging method is that it offers clear visibility into your outstanding debts. While that is really beneficial, at times, it can be time-consuming to maintain and might not forecast the future that well. That’s just one of its cons.
Now, to calculate the total amount of bad debt expense, the estimated percentages are then multiplied by the total amount of receivables within that time frame and added together. This is often called a very “proactive” way to approach this situation. It offers a structured way to predict the amount of receivables that might not be collected. This can be best understood with an example, right? So, let’s look at the table below.
C. Historical Data Analysis
Historical data analysis, in simple words, is the method that helps to analyze historical data on bad debt expenses in order to pinpoint trends and patterns. Moreover, this information can be further used to predict and forecast any future bad debt expense on identical conditions.
D. Credit Risk Assessment
This is a very common method which involves evaluating the creditworthiness of a person before a business chooses to extend credit. Many do it through credit checks, financial statement analysis, among many other methods. Several advanced businesses use credit scoring models that help to assess numerous factors to predict the likelihood of whether the customer they are going to extend credit to has the potential to default on their payment.
Confused about bad debt expense calculation methods?
Ask our accountants!
Practical Tips for Estimating Bad Debt Expense
Now that you are aware what a bad debt expense is, and its methods of estimation – here’s a brief rundown of practical, actionable tips that can help you estimate it.
Regular Review of Accounts Receivable
- Get a consistent schedule: You should always review your accounts receivable aging report to understand and pinpoint any overdue or potentially uncollectible amounts. This can help you intervene quicker and make collection efforts where there is still time on your hands.
- Turn your eyes to high-risk accounts: Always make it a habit to prioritize the analysis of accounts that have a history of giant outstanding balances, delayed payments, or consumers who have a plummeting credit score.
Collaboration between Finance and Sales Departments
- Open communication: The first point, as indicated, must be to have clear, transparent communication between your finance and sales teams. “Sales” can offer you some inside knowledge about the payment patterns, customer relations, and potential risks associated with certain customers.
- Joint credit risk assessment: Work together to concoct credit guidelines and put procedures in place for both new and current clients’ credit risk assessments.
Usage of Software Tools for Analysis
- Accounting software integration: There are multiple accounting software solutions which support built-in features that help manage accounts receivable and give a solid estimate of bad debt expense. You should always leverage tools to automate calculations and produce reports for more promising insights. Read more about NetSuite modules.
- Advanced analytics tools: To better understand customer creditworthiness and foresee future bad debt, bigger companies may want to investigate credit scoring models or advanced analytics tools.
Monitoring Economic Indicators
- Keep yourself updated: Recognize the general economic trends as well as industry-specific elements that may influence consumer payment patterns and raise the possibility of bad debt.
- Always adjust estimations: On the basis of economic changes alongside any other external factor, make sure that you are adjusting your bad debt expense estimates. It is always better to be safe than sorry.
Importance of Accurate Estimation
For multiple reasons, it is essential to estimate bad debt expenses accurately. Here is a detailed overview of the same:
- Impact on Financial Statements: This shows the true integrity of the financial statements by exhibiting the raw reflection of a business’s profits and the real asset values. In fact, this modification helps to offer a more realistic depiction of the business’s financial situation. Who is this important for? Well, in simple words, it is highly important for both internal evaluations and external reporting. Read more about financial audits.
- Management Decision Making: You get streamlined decision-making if you have precise, to-the-point bad debt estimates. In the meantime, this helps management teams understand the very financial impact of credit risks. After they have fully fathomed it, they can make wise decisions about resource allocation, credit policies, and more. This is high-end information that directly impacts a company’s priorities.
- Investor Confidence: Many don’t know but investor confidence is just as important here as any other factor. Accurate financial reporting, which also includes real estimates of bad debt, can help to maintain or in fact, boost investor confidence. Investors are more likely to maintain or grow their investment when they have confidence in the accuracy of a business’s financial statements. This is because investors provide the much needed funds for the growth and stability of the business. Learn more about short term investments.
Final Thoughts and Key Takeaways
Selling to customers on credit always comes layered with an exposure to risk.
What if they don’t end up paying back the sum? Not to mention, this is something all businesses encounter quite occasionally.
A bad debt expense impacts the balance sheet and income statement of a company, on a whole.
To showcase a very true side of the financial performance of a company, businesses need to manage their bad debt expense well or they can be trapped.
Regardless of whether you are a business owner, CFO, or someone just deeply interested in accounting, then having a clear idea of what this term means can create a larger impact on your financial situation.
Still have unanswered questions on your mind? We can help. Get direct assistance from accounting and bookkeeping experts who have more than 12 years of experience in this field. Never leave the room without answers. Get in touch now.
Frequently Asked Questions
Ques. How to calculate bad debt expense using the aging method?
Ans. The aging method, which first came into effect in 1934, is one of the most used and easiest methods to calculate bad debt expense. Let’s simplify it for you. The accounts receivable aging method is all about balancing the uncollectible accounts receivable. Often, it is done by showing the percentage of doubtful debts over a given time frame.
Ques. How to calculate bad debt expense using allowance method?
Ans. The allowance method helps to evaluate bad debt by separating a segment of total accounts receivable on the basis of predicted non-payments. Businesses usually analyze the expected percentage of unpaid orders and then assign separate funds for them based on the information retrieved.
If you want to find the sum, here’s how you can do it. The estimated bad debts are divided by the total projected sales to determine the allowance for bad debts. Fast forward, the percentage is then multiplied by 100.
Here’s the formula you can use:
(Anticipated bad debt / Total amount of expected sales) x 100 = Bad debt allowance
Ques. What is the percentage of the bad debt formula?
Ans. The percentage of bad debt formula can be shown as:
Percentage of bad debt = Total bad debts / Total credit sales
Despite knowing this formula, always remember that this isn’t honestly a very reliable method to forecast future bad debts, specifically if you have not been in the business arena for long enough, or if this one giant bad debt is actually disfiguring your bad debt percentage.