You’re staring at your financial statements, and the numbers don’t add up.
Your Cost of Goods Sold looks wrong, and you’re worried about what that means for your taxes and profitability.
This comprehensive guide will show you exactly how to calculate, track, and manage COGS accurately so you can make confident financial decisions and avoid costly errors.
We’ll walk you through everything from basic formulas to advanced tax strategies, with real-world examples and troubleshooting guidance for common software issues.
Let’s get started.
Key Takeaways
- COGS represents direct production or purchase costs, and calculating it accurately is essential for correct gross profit margins, pricing decisions, and tax reporting.
- COGS and operating expenses are not interchangeable—misclassifying them can distort financial statements and lead to IRS compliance issues.
- COGS = Beginning Inventory + Purchases – Ending Inventory, but accuracy depends heavily on consistent and correct inventory valuation.
- FIFO, LIFO, and Weighted Average dramatically change reported profit, taxable income, and balance sheet values; the right method depends on industry, pricing trends, and compliance requirements.
- Software setup errors are a major source of COGS mistakes, especially in QuickBooks, NetSuite, and other accounting systems; correct item configuration is crucial.
- Optimizing COGS improves cash flow and profitability, and reviewing costing methods, software settings, and tax strategy regularly can prevent expensive errors.
What Is Cost of Goods Sold (COGS)?
Let’s start with the foundation—understanding what COGS actually means and why it matters to your business.
Cost of Goods Sold (COGS) represents the direct costs of producing or purchasing the goods your business sold during a specific period.
This includes materials, labor directly tied to production, and manufacturing overhead, but excludes indirect expenses like marketing, rent, or administrative salaries.
Here’s why COGS matters for your business beyond just being another accounting term.
- First, it directly impacts your gross profit margin—the money left after subtracting COGS from revenue determines whether you’re actually profitable.
- Second, COGS is tax-deductible, which means calculating it correctly can significantly reduce your taxable income.
- Third, understanding your COGS helps you make smarter pricing decisions, identify cost increases early, and manage your cash flow more effectively.
If you’re manufacturing products or managing inventory across multiple locations, Xero will force you to bolt on $100-200/month in third-party apps that still won’t talk to each other properly.
Also Read: Odoo Accounting For Manufacturing
COGS vs. Operating Expenses: What's the Difference?
Many business owners confuse COGS with operating expenses, but they’re fundamentally different.
COGS includes only direct costs tied to producing goods sold – think raw materials, factory labor, and manufacturing supplies.
Operating expenses cover everything else your business needs to function: rent, utilities, marketing, administrative salaries, and office supplies.
Here’s a quick comparison:
| COGS (Direct Costs) | Operating Expenses (Indirect Costs) |
|---|---|
| Raw materials | Rent and utilities |
| Direct labor (production) | Marketing and advertising |
| Manufacturing overhead | Administrative salaries |
| Packaging materials | Office supplies |
| Freight-in costs | Professional fees |
The distinction matters because COGS appears before gross profit on your income statement, while operating expenses appear after.
This placement affects how investors and lenders evaluate your business’s profitability. According to IRS Publication 334, properly categorizing these costs is essential for accurate tax reporting.
When you track direct costs versus indirect costs correctly, you can identify exactly where your money goes and make informed decisions about pricing, inventory management, and business growth.
The Cost of Goods Sold Formula & How to Calculate COGS
Now that you understand what COGS is, let’s break down the formula and calculation process.
Ever feel confused about where to start with COGS calculations? You’re not alone—but the basic formula is actually straightforward once you understand its three components.
The Standard COGS Formula Explained
The cost of goods sold formula follows this structure:
COGS = Beginning Inventory + Purchases – Ending Inventory
Inventory Valuation Methods (FIFO, LIFO, & Weighted Average)
Now that you understand the COGS formula, let’s tackle one of the most critical decisions affecting your calculation—how you value your inventory.
Which items did you sell first—the ones you bought last month or last year? Your answer to this question, called your inventory valuation method, can swing your tax bill by thousands of dollars and change how your business appears on financial statements.
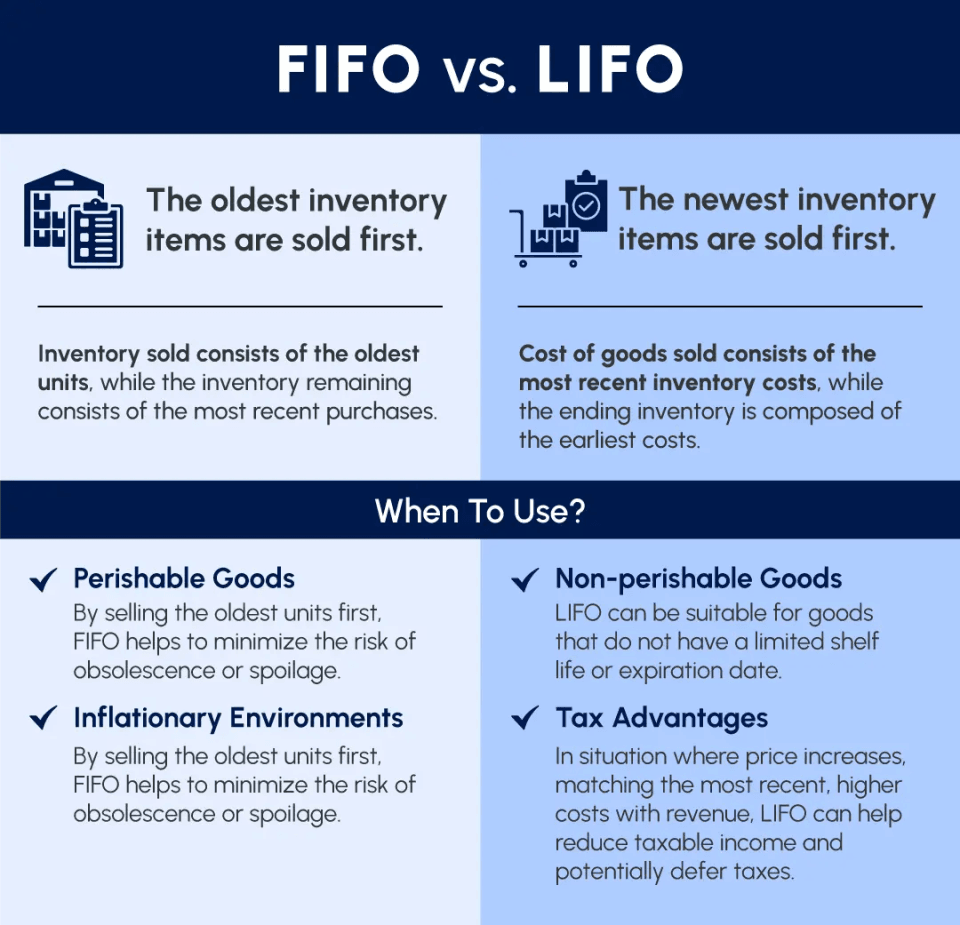
FIFO (First In, First Out) Method
FIFO assumes you sell your oldest inventory first, just like a grocery store rotates milk to sell the oldest cartons before they expire. Under FIFO, your cost of goods sold reflects the prices you paid for your earliest purchases, while your ending inventory is valued at your most recent costs.
Here’s why this matters: During periods of rising prices (inflation), FIFO results in lower COGS because you’re recording older, cheaper costs. This means higher gross profit, higher net income, and higher taxes. However, your balance sheet shows inventory valued at current market prices, giving a more accurate picture of what you could sell it for today.
LIFO (Last In, First Out) Method
LIFO flips the script—it assumes you sell your newest inventory first. When prices are rising, this method results in higher COGS because you’re recording recent, more expensive purchases. That means lower taxable income and potentially significant tax savings.
But there’s a catch: the IRS requires special permission to use LIFO, and you must file IRS Form 970. Plus, LIFO isn’t permitted under International Financial Reporting Standards (IFRS), so if you do business internationally or plan to in the future, you’ll face complications. Your ending inventory will also appear undervalued on your balance sheet since it reflects old, outdated costs.
Weighted Average Cost Method
LIFO flips the script—it assumes you sell your newest inventory first. When prices are rising, this method results in higher COGS because you’re recording recent, more expensive purchases. That means lower taxable income and potentially significant tax savings.
But there’s a catch: the IRS requires special permission to use LIFO, and you must file IRS Form 970. Plus, LIFO isn’t permitted under International Financial Reporting Standards (IFRS), so if you do business internationally or plan to in the future, you’ll face complications. Your ending inventory will also appear undervalued on your balance sheet since it reflects old, outdated costs.
Which Inventory Method Should You Choose?
Your choice depends on several factors:
- Choose FIFO if: You sell perishable goods, want higher reported profits for investors or loans, or do international business
- Choose LIFO if: You’re in the U.S., face rising costs, and want to minimize taxes (but can handle the complexity)
- Choose Weighted Average if: You sell bulk commodities, want simplicity, and prefer stable, predictable costs
Best COGS Tracking Software & Tools
Now that you understand COGS in financial statements, let’s look at the tools that make tracking it easier and more accurate.
Are you still calculating COGS manually in spreadsheets? If so, you’re probably spending hours on calculations that software can handle in seconds—and you’re risking errors that could cost you thousands in taxes or lost profit opportunities.
1. QuickBooks for COGS Management
QuickBooks Online and Desktop remain the most popular choices for small to mid-sized businesses. QuickBooks automatically calculates COGS when you enable inventory tracking and create sales transactions using inventory items.
Your COGS appears correctly on profit and loss reports, and inventory values update on your balance sheet.
Common issues we see: Users often set up items as “service” instead of “inventory,” causing QuickBooks to bypass COGS tracking entirely.
Another problem – entering item costs after creating sales transactions results in zero or incorrect COGS.
The fix requires adjusting historical transactions, which gets messy fast. According to Intuit research, 38% of businesses experience COGS discrepancies due to improper item setup.
2. NetSuite COGS Tracking
NetSuite offers enterprise-grade COGS management for larger businesses or those with complex needs.
NetSuite handles multi-location inventory, landed costs (freight, duties, customs), sophisticated costing methods, and real-time inventory tracking across warehouses. It automatically calculates COGS based on your chosen method and provides drill-down visibility into cost components.
The trade-off?
NetSuite costs significantly more and requires professional implementation. But if you’re managing inventory across multiple locations, dealing with international shipping, or need advanced reporting, NetSuite’s capabilities justify the investment.
3. Zoho Books & Other Alternatives
Zoho Books provides a middle ground—more powerful than basic accounting software but less expensive than NetSuite. It handles inventory tracking, COGS calculation, and integrates with e-commerce platforms like Shopify and Amazon.
Other solid alternatives include Xero (great for small businesses, excellent bank feeds), FreshBooks (best for service businesses adapting COGS concepts), and Cin7 (specialized inventory management that integrates with QuickBooks).
READY TO GET YOUR COGS RIGHT?
Here’s the thing: knowing what to do and actually implementing COGS correctly are two different challenges.
The mistakes we’ve outlined aren’t theoretical—they’re errors we fix regularly for businesses that thought they had everything set up correctly.
Book a free 30-minute COGS Review with our CPAs. We’ll identify calculation errors, software configuration issues, and tax optimization opportunities you’re missing.
No pressure, no sales pitch – just honest feedback about your COGS accuracy.











