1. Gross income reflects total revenue before deductions, while net income is calculated after accounting for all expenses, including taxes, interest, and operating costs.
2. Understanding the distinction helps businesses strategize, monitor performance, and present accurate financial reports for stakeholders, aiding in investment and operational decisions.
3. Gross income includes revenue from all sources, while net income reveals profitability after deducting operating and other costs, making it vital for long-term financial planning
Net income and gross income are two of the fundamental cornerstones of financial analysis.
In fact, they are highly integral to any business since they give business owners an idea of how their company is generating money. Furthermore, managers have no certain way of knowing whether to raise their sales or cut costs in order to increase profitability.
But, if they have a fair understanding of their net income and gross income, it becomes a breeze to understand their current financial standpoint.
Why is Net Income and Gross Income important in Financial Analysis?
Gross and net income help understand the overall earning capacity of a business. As gross income alone cannot show you the whole picture, you need to have a fair understanding of net versus gross income.
While gross income indicates how well a business has been selling, net income exhibits how well it has balanced the costs and managed to stay profitable. It is one of the key ways to analyze the company’s financial performance from the ground up.
Let’s understand this through a simple example. For instance, a company may definitely have a high gross income due to all the sales it has been making on the run, but its net income can be low due to the increased operating expenses.
This is how a company recognizes the areas that need redesigning or immediate attention. Moreover, they are also integral for budgeting, business performance, and wise financial decision-making.
What is Gross Income?
Remember the time you received your first paycheck? Was the amount a little or a lot less than what you expected the total to be? That’s where people think, “Hey, how does the money promised differ so largely from what I received?” Well, that analogy works for gross income too.
Gross income, in terms of businesses, shows the company’s earnings before there have been any expenses, including but not limited to direct costs related to the production of goods, or indirect costs, such as the wages for staff members. As a result, it is basically the total profit a business makes from the sales it has made during a given period.
What can you do for better payroll management?
Calculating Gross Income: Individual vs. Business
For individuals, gross income is far more than salaries or wages. It can also widely include alimony, capital gains, rental income, dividends, tips, interest, and pensions. In fact, the figure you get, minus the particular tax deductions can form the adjusted gross income (AGI) on tax returns. For non-tax purposes, such as a loan application, gross income is the total earnings prior to expenses and taxes.
In businesses
In businesses, gross income is just slightly different. If you look closely at an income statement, it shows gross income minus the cost of goods sold. Here’s the formula of gross income:
Gross income = Gross revenue – COGS where COGS means Cost of Goods Sold
Often referred to as the gross margin, it shows the profit obtained from services or products after addressing direct costs. Although gross income does show the direct costs of production, it still does not include selling, taxes, administrative fees, or other operating costs.
Want expert help calculating your gross and net income?
Connect with us
Gross Income Calculation Example
Let’s understand gross income better with an example. Imagine a company, ABZ Contractors, has a gross revenue of $2,000,000. This is how the breakdown looks like:
- Cost of raw materials: $200,000
- Cost of supply: $80,000
- Cost of equipment: $400,000
- Costs of Labor: $250,000
- Packaging and shipping: $150,000
Therefore, let’s now calculate the gross income for the above information.
Hence, Gross Income = ($2,000,000) – ($200,000 + $80,000 + $400,000 + $250,000 + $150,000)
This is the result that we get:
= ($2,000,000) – ($1,080,000) = $920,000
Therefore, the gross income of the company is $920,000.
General Template of Gross Income
Here’s how a general template of Gross Income looks like.
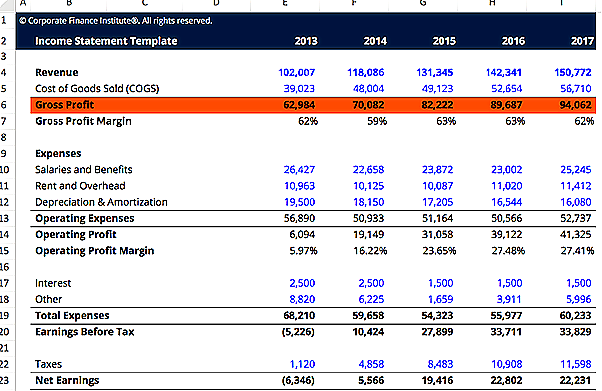
To download free excel gross income template, click here.
So far, we have seen what gross income is and how to calculate gross income. Now let’s learn about net income.
What is Net Income?
Net income can be evaluated by deducting income taxes, operating expenses, depreciation, and interest on loans or debts from the earnings of a company. Now, this is largely a figure that can include anything between salaries, wages, raw materials, taxes, and cost of goods sold.
If you look at a company’s income statement, net income basically shows the total profit following all the deductions in gross income. As a result, the amount you get can be assigned to several motives, including but not limited to dividend distribution to shareholders, paying the salaries of employees, reinvesting back to the business, or simply just adding on to the savings.
There are many who also refer to net income as net earnings or net profit. At times, many also choose to call it the “bottom line” since it places at the bottom of the income statement.
The formula for calculating net income is:
Net Income = Revenue – Cost of Goods Sold – Expenses If you notice closely, the first part of the net income formula matches with the formula of gross income. Here’s another way to represent the net income formula:
Net income = Gross income – Expenses
When you put to use the formula above, you can determine the company’s net income for a given time frame whether it is monthly, quarterly, or annually.
Net Income Calculation Example
Let’s understand net income better with an example. Assume a business, let’s say, Jack’s Biker has been assessing their net income for the initial quarter of 2023. Here’s what their financial rundown looks like:
- Total revenue: $70,000
- Cost of goods sold: $25,000
- Utilities: $3,000
- Rent: $7,000
- Internet: $1,500
- Payroll: $12,000
- Ads: $2,000
This is where the business starts looking at their gross income, involving deduction of COGS from total revenue, just like this:
Gross income = $70,000 – $25,000 = $45,000
Following that, they start calculating the expenses for the quarter:
Therefore, Expenses = $3,000 + $7,000 + $1,500 + $12,000 + $2,000 = $25,500
Hence, the net income can be determined when you deduct these expenses from the gross income:
Net income = $45,000 – $25,500 = $19,500
Therefore, Jack’s Biker has a net income of $19,500 for the quarter.
General Template of Net Income
Here’s how a general template of net income looks like:
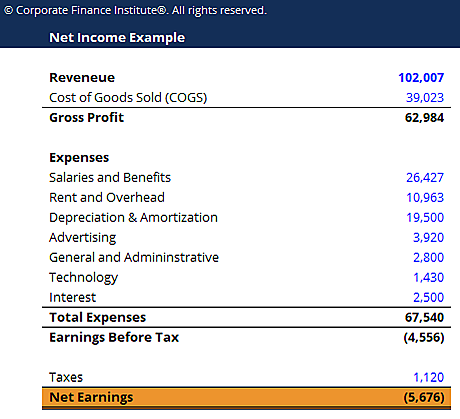
To download free excel net income template, click here.
Analyzing the Relationship between Net Income vs Gross Income
This is one of the critical areas to look at when you are trying to understand the financial health of your company. So, let’s look at how gross income and net income differ from each other.
Gross income is basically the business’s total revenue minus the cost of goods sold. For the most part, this is a measure of how effectively your business is using its resources to yield goods and count sales. On the other hand, net income is the real profit after you subtract all the baggage of expenses and taxes. To reflect, this depicts the business’s actual profitability after accounting for the operations it endures.
But, do you know what impact do changes in gross income have on net income? Well, an increase in gross income, considering that all the expenses are constant, generally translates into a rise in net income (and vice versa).
Factors that affect the Relationship
- External Factors (Market conditions or economic trends)
- Efficiency Improvements
- Operating Expenses
Case Study Showing the Relationship Between Gross and Net Income
Let’s consider a retail company called ABZ Ltd. Only recently, they have increased sales, resulting in a higher gross income. However, they also saw a significant rise in rent and employee salaries. This, in return, spiked the operating expenses side by side. This means that even with the increased gross income, the additional expenses prevented the net income from growing proportionately.
Importance of Net Income and Gross Income in Financial Statements
Gross vs net income is incredibly integral in a business’s financial statements, especially the income statement and balance sheet. In fact, they are considered very important to several stakeholders, such as lenders, investors, and analysts. For them to obtain a complete picture of their financial assessments, these are the numbers that matter most.
Role in Income Statements and Balance Sheets
- Income statement: The gross income can be found on the income statement as the total revenue deducted from the cost of goods sold (COGS). On the flip side, net income is the profitability of a business after it has accounted for all the taxes, expenses, and more.
- Balance sheet: Although you cannot find the net income directly on the balance sheet, it largely affects shareholder equity. As part of the shareholder equity, the net income impacts the retained earnings. Mainly, this is because it is responsible for depicting the collective profits retained in the business after the dividends are paid and released.
Read more about how to calculate retained earnings on a balance sheet
Key Metrics and Ratios
Any discussion on Net Income and Gross Income is incomplete without some key metrics.
- Gross Margin Ratio = Net sales – COGS / Net sales.
- Net Profit Margin (%) = Net Income ÷ Revenue
- Return on Equity (ROE) = Net income / Average shareholder’s equity
- Earnings Per Share (EPS) = Net income – Preferred dividends / End-of-period common shares outstanding
Want help calculating key financial metrics?
Our experts are here!
4+3 Tips for Maximizing Net Income and Gross Income
Maximizing your gross income and net income is highly essential for financial growth. Here’s how you can maximize both.
- Gross Income:
a) Refine market strategies: Start investing in proper marketing efforts to engage with your target audience. In return, this can help you boost sales and also improve brand awareness.
b) Diversify your revenue sources: This is a way to begin tapping into new products, markets, and services that are in line with your expertise. This is just another way to boost brand visibility and customer reach.
c) Use strategic pricing: You must set prices that reflect the value offered. Besides, conduct comprehensive market research to understand market expectations.
d) Boost customer satisfaction: You should always prioritize outstanding customer service. Happy customers are more likely to return and refer more of their friends and acquaintances. - Net income:
- a) Expense management: Make sure to keep a close eye on expenses and try to identify saving opportunities. This is where you should identify non-essential costs that need a permanent trim.
- b) Supplier negotiations: Negotiate better agreements with suppliers in order to lower costs.
- c) Adopt energy efficiency: Incorporate certain energy-saving practices to trim utility expenses, such as optimized climate control.

4 Common Pitfalls to Avoid in Financial Analysis
For effective and appropriate decision-making, you need to avoid the common pitfalls associated with financial analysis. Here are some of them:
- Neglecting qualitative factors: If you solely rely on quantitative data, there’s no doubt that you will soon miss out on qualitative aspects, such as brand strength, management quality, and many more subtle areas.
- Highly reliant on historical data: While specific historical data can be significant, relying solely on it can definitely be misleading. You always have to know that markets and their conditions will vary.
- Ignoring non-financial metrics: There are a lot of metrics that you need to wrap your head around. Employee engagement and customer satisfaction, among others, can indirectly impact financial performance.
- Inefficient scenario analysis: If you fail to take into account the many “what-if” scenarios, especially during moments of uncertainty, then it can leave your company unprepared for probable risks.
In Summing Up
Gross income, as the name already suggests, depicts the total revenue a business earns from its operations before any deductions, such as taxes, have been made. This is a measure that helps recognize a business’s ability to yield sales and simultaneously manage production costs. Net income is just the opposite side of the same coin. It is basically a definitive earnings figure.
More precisely, it shows the actual profit a company has retained after accounting for its expenses, additional income streams, and losses. It is a measure that helps us understand how profitable a company is after it has paid off all additional expenses.
Frankly, both gross vs net income are integral to understanding how a company is doing financially. It is where investors and analysts look at before making a big decision. Together, these metrics can give you the whole picture of a company’s financial standing.
Still confused about the terms and how they are applicable in real life? Talk to us. Our in-house accounting and bookkeeping experts have more than 12 years of experience and can give you all the clear answers you need. Get in touch today.












